Revealing the Mysteries of the Mind Through Quantitative EEG Brain Mapping Techniques in Mental Health Evaluation
Revealing the Mysteries of the Mind Through Quantitative EEG Brain Mapping Techniques in Mental Health Evaluation
Blog Article
Comprehending the human brain is a complex endeavor, especially when it comes to mental health. Traditional methods of assessment frequently depend on interviews and surveys, which can occasionally overlook important details about how the brain operates. This is where quantitative brainwave analysis, or qEEG, enters into the picture. qEEG is a specialized technique that assesses neural signals in the brain. By analyzing these neural patterns, psychological health professionals can gain important insights into a individual's mental state, aiding to improve assessment and treatment.
qEEG functions by applying small sensors on the scalp to capture neural activity. These electrodes measure neural signals produced by neurons, the cells in the brain that interact with each other. The information collected is then processed and displayed as a series of waveforms. Each type of brainwave—such as α, beta, delta, and theta—corresponds to various psychological conditions and activities. For instance, α oscillations are commonly linked with relaxation, while beta waves are associated to active thinking and issue resolution. By analyzing these trends, clinicians can detect abnormalities that may suggest mental health issues.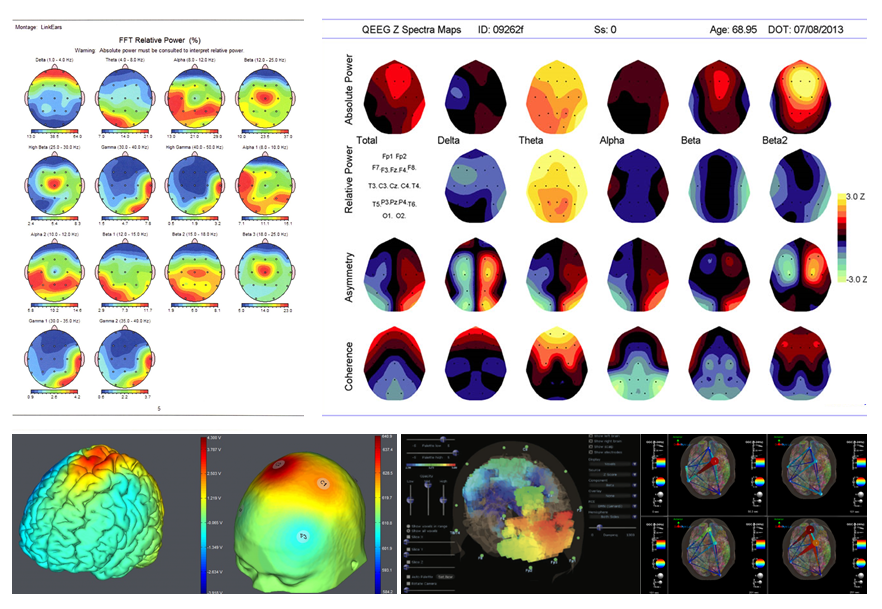
One of the significant benefits of qEEG is its ability to provide objective data. In contrast to traditional assessments that rely on subjective reports from patients, qEEG offers a clear picture of brain activity. This clarity can assist minimize prejudices in assessment and result to more accurate treatment strategies. For example, if a patient is experiencing anxiety, qEEG can show particular patterns of brain activity that are associated with anxiety disorders. This biofeedback for mental clarity information enables psychological health experts to customize treatments more effectively, whether it be through counseling, pharmaceuticals, or alternative approaches.
Additionally, qEEG can be particularly useful in tracking intervention advancement. By conducting qEEG assessments at different stages during treatment, clinicians can monitor changes in neural activity over time. This ongoing evaluation helps ascertain if a intervention is working or if modifications are required. For instance, if a client is not reacting to a particular medication, qEEG may show that their brain activity has not changed in a way that indicates improvement. This response cycle can lead to more personalized and effective mental health care.
In summary, qEEG brain mapping is a powerful instrument in the field of psychological health evaluation. By offering objective data about neural function, it enhances the comprehension of different psychological health disorders. This method not only assists in accurate assessment but also assists in tracking intervention success. As psychological health experts persist to explore the potential of qEEG, it holds promise for improving the lives of people dealing with psychological health issues. With continuous investigation and progress in techniques, the mysteries of the brain may turn clearer, resulting to better results for those in need of assistance.